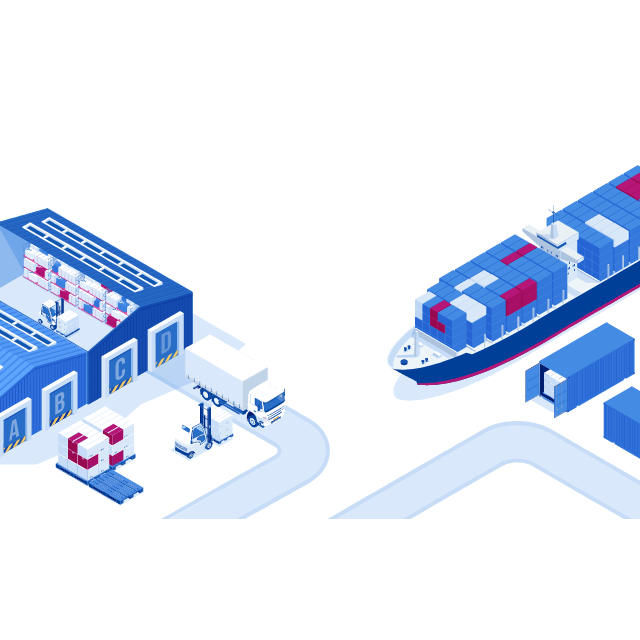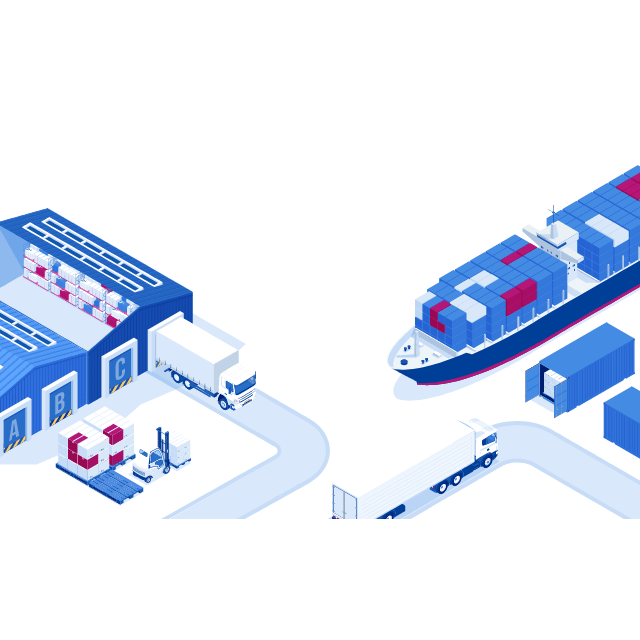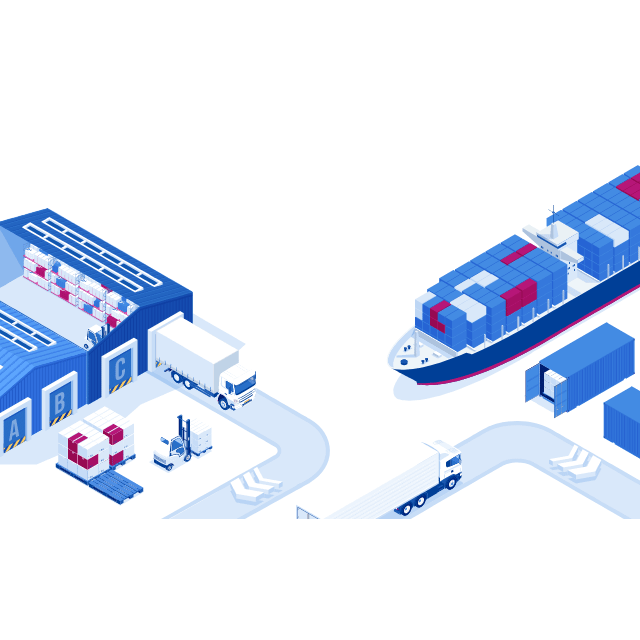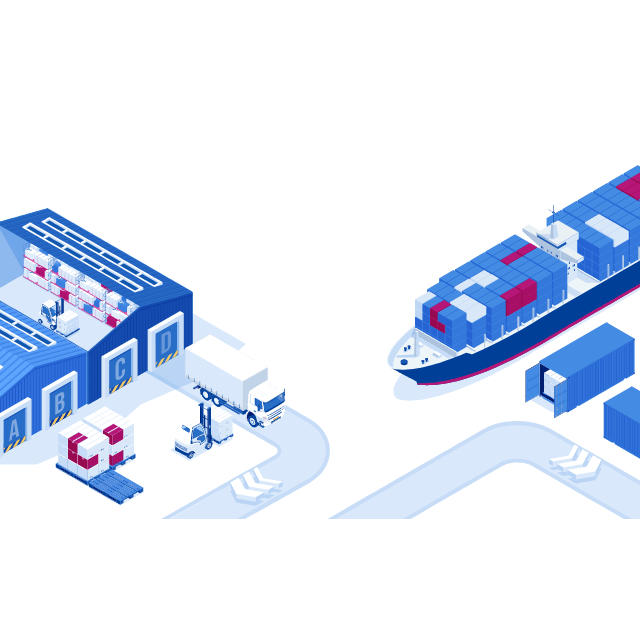
Supply chain refers to the interconnected network & stakeholders as of individuals, organizations, and resources involved in the production and delivery of a product or service. It encompasses all the activities required to bring a product from raw materials to the final customer, including sourcing of materials, manufacturing, transportation, storage, and distribution.
It’s a complex system that involves many different participants, each with their own goals, processes, and challenges. Effective supply chain management requires coordination and collaboration among all these participants to ensure that products are delivered on time, at the right cost, and to the right quality.
The goal of supply chain management is to optimize the overall performance of the supply chain, balancing the conflicting priorities of cost, service, and risk. This involves making decisions about where to source materials, how to transport products, and when to release products for sale, among other things. Supply chain management is a critical function for companies in many industries, as it can have a significant impact on their competitiveness, profitability, and overall success.
There have been several tendencies in supply chain management in recent years, including:
- Increased focus on sustainability and corporate social responsibility: Companies are increasingly looking for ways to reduce their impact on the environment and to ensure that their suppliers adhere to ethical and environmental standards.
- Greater use of technology: Technology such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) is being increasingly used to optimize supply chain processes, improve visibility, and increase efficiency.
- Emphasis on resilience and risk management: Companies are seeking to build more resilient and flexible supply chains in order to better manage risks and minimize disruptions.
- Growing importance of data and analytics: The use of data and analytics is becoming increasingly critical in order to make informed decisions, monitor performance, and identify areas for improvement.
- Shift towards on-demand and flexible manufacturing: Companies are looking for ways to respond more quickly to changing customer demands, and are adopting on-demand and flexible manufacturing models to achieve this.
- Rise of new and innovative business models: Companies are exploring new business models such as circular economies, sharing economies, and platform-based businesses in order to create more sustainable and efficient supply chains.
These tendencies are driven by a range of factors, including the changing needs and expectations of customers, the increasing complexity of global supply chains, and the need to respond to economic, political, and environmental challenges.
The tendencies in supply chain management can vary between the private sector and the government, although there are some similarities. Some of the tendencies in the private sector and the government include:
Private Sector:
- Increased focus on sustainability and corporate social responsibility.
- Growing importance of data and analytics in decision-making.
- Shift towards flexible and on-demand manufacturing models.
- Focus on cost-efficiency: Companies in the private sector are driven by the need to improve efficiency and reduce costs in order to remain competitive.
- Emphasis on customer satisfaction: Private sector companies place a high priority on meeting customer demands and delivering high-quality products and services.
- Adoption of new technologies: The private sector is known for its willingness to invest in new technologies, such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, to improve supply chain processes.
Government:
- Emphasis on national security and disaster preparedness, with a focus on building resilient and secure supply chains.
- Growing importance of public-private partnerships to address complex supply chain challenges.
- Focus on ensuring compliance with regulations and standards, such as those related to environmental protection and cybersecurity.
- Focus on transparency and accountability: Governments place a strong emphasis on transparency and accountability in their supply chain processes, in order to ensure that taxpayer money is used effectively.
- Investment in infrastructure: Governments often invest in infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and ports, to improve the efficiency and competitiveness of their supply chains.
- Support for local suppliers: Governments may also prioritize the use of local suppliers and businesses to support their local economies.
Overall, both the private sector and government have a shared interest in building efficient, resilient, and sustainable supply chains. However, the specific priorities and tendencies will vary depending on the sector and the goals of each organization.